403 Forbidden with Spring Security
TIP
You may think there's no wrong, but 403 Forbidden appeared.
Don't be in panic. Check step by step!
I'll add other cases whenever I encounter 403.
Check Config Settings
spring security can authorize for each uri.
Therefore, if uri is wrong or misauthorized uri can be a problem.
Here is an example.
Assume uri /main should be opened to everyone.
Therefore, /main should be permitAll().
But we cannot find the uri /main in this codes below.
Then, the uri /main is belong to anyRequest condition, and only USER can be reached. Others will meet 403 Forbidden
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.httpBasic().disable() // diabled. rest api settings
.csrf().disable() // rest api. no csrf
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS) // using jwt token, no session needed.
.and()
.authorizeRequests() // check for requests
.antMatchers("/signin", "/signup", "/login").permitAll() // everyone can call this uri
.antMatchers("/test").hasAnyRole("USER", "ADMIN") // only user and admin can call
.anyRequest().hasRole("USER") // other requests are blocked except user
.and()
.addFilterBefore(new JwtAuthenticationFilter(jwtTokenProvider), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class); // jwt token Filter is added before id/password Filter
}
// code: https://sybarits.github.io/2020/11/08/rest-api-security.html
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Check Filter
Look at the code above. JwtAuthenticationFilter is added as Filter.
Code lines of this filter look like this.
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
// get token info
String token = jwtTokenProvider.resolveToken((HttpServletRequest) request);
// if valid token, get auth info
if (token != null && jwtTokenProvider.validateToken(token)) {
// add auth info to context
Authentication auth = jwtTokenProvider.getAuthentication(token);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(auth);
}
// do Filter
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
The result of this code looks like this. The debugging point is on 12th line(highlighted line). 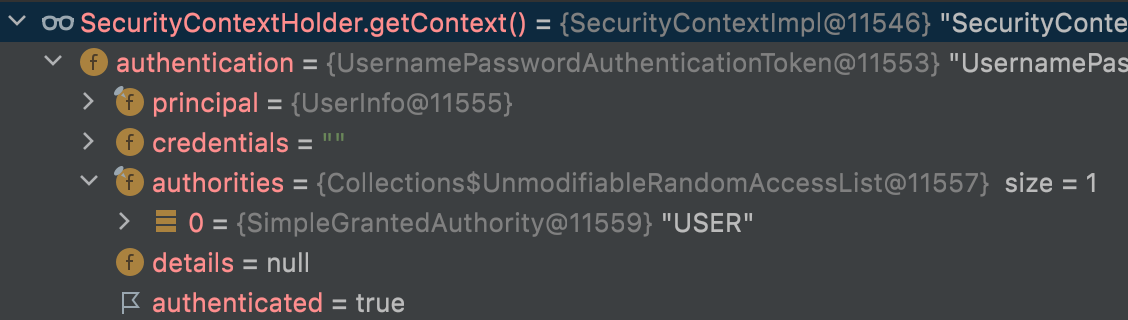 This request is authenticated from valid token, and you can see
This request is authenticated from valid token, and you can see USER on authorities parameter.
At this point, you should know something is wrong!
From token, String(USER) role is found, and USER is configured on method configure above.
It seems same, so you may think this request should be passed, but wrong.
In Spring security, if role is USER on configure method, the token should have ROLE_USER.ROLE_ prefix is needed!
If this role is in Database, also should be stored like ROLE_USER.
You may change prefix from ROLE_ to other by using Auth Mapper.
In Short,
At configure method, no need to use ROLE_ prefix. In token, ROLE_ prefix is needed like ROLE_ADMIN. If you use database when filtering with role name, ROLE_ prefix is needed.
